Vitamin C
Ascorbic Acid
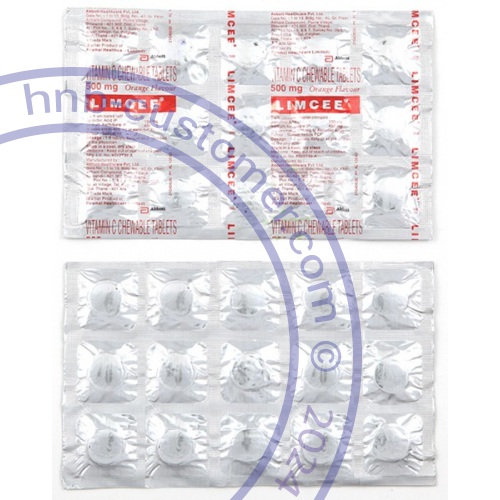

Ascorbic acid tablets
What is this medicine?
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) occurs naturally in foods such as citrus fruit, tomatoes, potatoes, and leafy vegetables. Vitamin C is important for bones and connective tissues, muscles, and blood vessels. Vitamin C also helps the body absorb iron, which is needed for red blood cell production.
Ascorbic acid is used to treat and prevent vitamin C deficiency.
Ascorbic acid may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide.
What should I tell my health care provider before I take this medicine?
You should not use ascorbic acid if you have ever had an allergic reaction to a vitamin C supplement.
Ask a doctor or pharmacist about using ascorbic acid if you have:
-
kidney disease or a history of kidney stones;
-
hereditary iron overload disorder (hematochromatosis); or
-
if you smoke (smoking can make ascorbic acid less effective).
Your dose needs may be different during pregnancy or while you are breast-feeding a baby. Do not use ascorbic acid without your doctor's advice in either case.
How should I use this medicine?
Use exactly as directed on the label, or as prescribed by your doctor. Do not use in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended.
The recommended dietary allowance of vitamin C (ascorbic acid) increases with age. Follow your healthcare provider's instructions. You may also consult the Office of Dietary Supplements of the National Institutes of Health, or the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Nutrient Database (formerly "Recommended Daily Allowances") listings for more information.
Drink plenty of liquids while you are taking ascorbic acid.
The chewable tablet must be chewed before you swallow it.
Ascorbic acid gum may be chewed as long as desired and then thrown away.
Do not crush, chew, or break an extended-release tablet. Swallow it whole.
Measure liquid medicine with a special dose-measuring spoon or medicine cup. If you do not have a dose-measuring device, ask your pharmacist for one.
Keep the orally disintegrating tablet in the package until you are ready to take it. Use dry hands to remove the tablet and place it in your mouth. Do not swallow the tablet whole. Allow it to dissolve in your mouth without chewing. Swallow several times as the tablet dissolves.
Store ascorbic acid at room temperature away from moisture and heat.
Do not stop using ascorbic acid suddenly after long-term use at high doses, or you could have "conditional" vitamin C deficiency. Symptoms include bleeding gums, feeling very tired, and red or blue pinpoint spots around your hair follicles. Follow your doctor's instructions about tapering your dose. Conditional vitamin C deficiency can be difficult to correct without medical supervision.
What if I miss a dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Do not take extra medicine to make up the missed dose.
What happens if I overdose?
Seek emergency medical attention.
What should I watch for while using this medicine?
Follow your doctor's instructions about any restrictions on food, beverages, or activity.
What side effects may I notice from this medicine?
Get emergency medical help if you have any of these signs of an allergic reaction: hives; difficult breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Stop using ascorbic acid and call your doctor at once if you have:
-
joint pain, weakness or tired feeling, weight loss, stomach pain;
-
chills, fever, increased urge to urinate, painful or difficult urination; or
-
severe pain in your side or lower back, blood in your urine.
Common side effects may include:
-
heartburn, upset stomach; or
-
nausea, diarrhea, stomach cramps.
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects.
What may interact with this medicine?
Other drugs may interact with ascorbic acid, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Tell each of your health care providers about all medicines you use now and any medicine you start or stop using.